Contract Agreement With Suppliers: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Collaboration
Supplier contracts are essential for any business looking to establish a stable and reliable supply chain. By outlining the terms and conditions of the agreement, both parties can ensure that they are on the same page and that their expectations are met. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of contract agreements with suppliers, covering everything from supplier evaluation and selection to contract management and compliance.
By understanding the key elements of a supplier contract and following best practices for negotiation and drafting, you can create an agreement that protects your interests and fosters a mutually beneficial relationship with your suppliers.
Supplier Evaluation and Selection
Finding the right suppliers is crucial for any business. They can impact your quality, cost, reliability, and sustainability. That’s why it’s essential to have a robust supplier evaluation and selection process.
There are several key criteria to consider when evaluating suppliers:
- Quality: Assess the supplier’s ability to meet your quality standards, including their manufacturing processes, materials, and quality control measures.
- Cost: Compare the supplier’s prices to others in the market, considering both upfront costs and ongoing expenses.
- Reliability: Evaluate the supplier’s track record for on-time delivery, responsiveness, and customer service.
- Sustainability: Consider the supplier’s environmental and social practices, including their commitment to ethical sourcing and waste reduction.
Supplier Due Diligence and Risk Assessment
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence and risk assessment. This involves:
- Background checks: Verify the supplier’s legal status, financial stability, and reputation.
- Site visits: Visit the supplier’s facilities to assess their operations and meet their team.
- Reference checks: Contact the supplier’s existing customers to gather feedback on their performance.
- Risk assessment: Identify potential risks associated with the supplier, such as supply chain disruptions, quality issues, or ethical concerns.
Contract Negotiation and Drafting
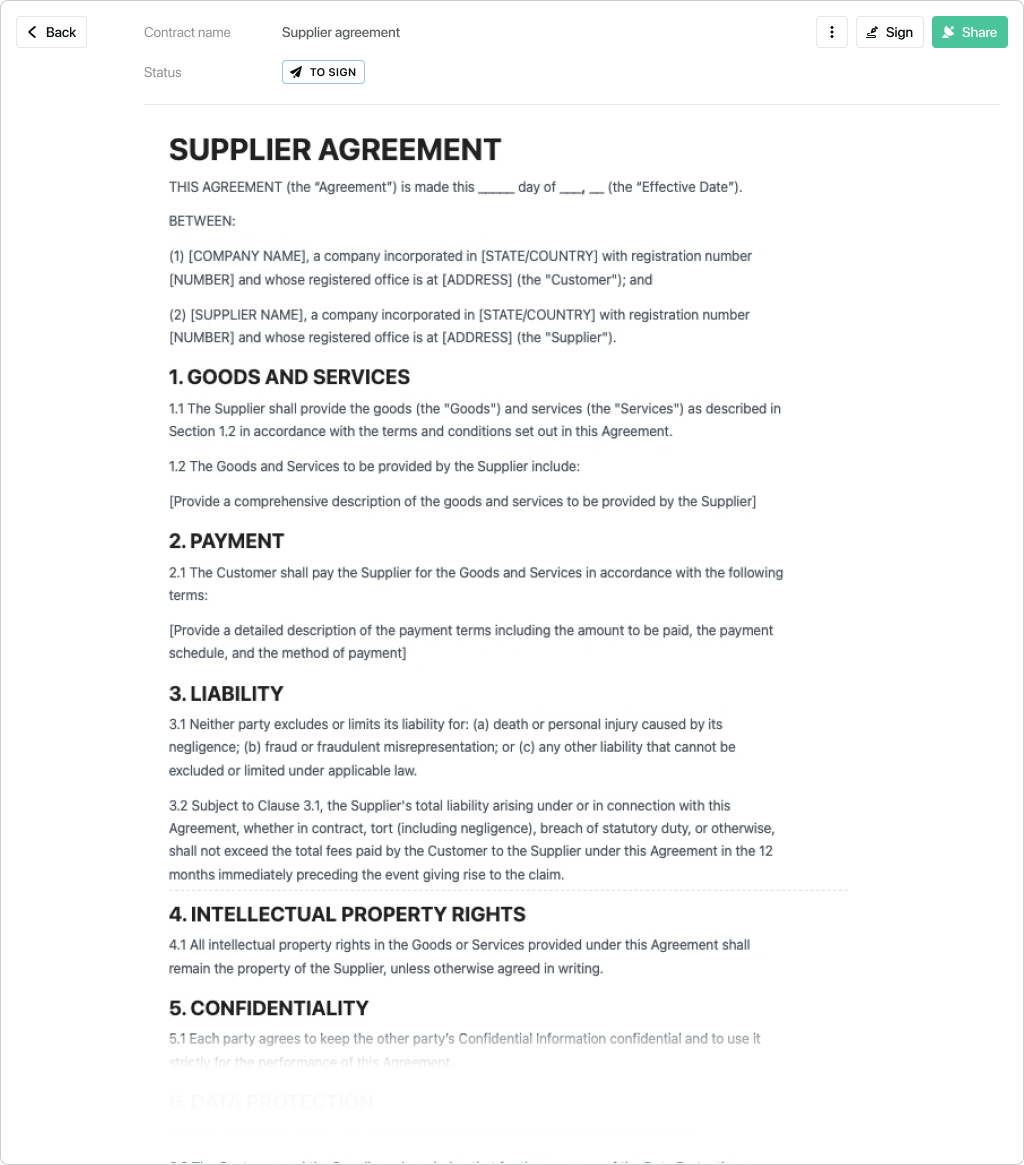
Contracts are an essential part of any business relationship. They set out the terms and conditions of the agreement between the two parties, and they help to protect both parties in the event of a dispute.
When negotiating and drafting a contract, it is important to consider the following key elements:
Scope of Work
The scope of work defines the specific services or goods that the supplier will provide. It should be clear and concise, and it should leave no room for ambiguity.
Payment Terms
The payment terms specify how and when the supplier will be paid. They should include the amount of the payment, the method of payment, and the due date.
Delivery Schedules
The delivery schedules specify when and where the supplier will deliver the goods or services. They should be realistic and achievable, and they should take into account the supplier’s production capacity.
Performance Guarantees
Performance guarantees are promises by the supplier that they will meet certain performance standards. They can include guarantees of quality, accuracy, and timeliness.
Essential Clauses
In addition to the key elements listed above, there are a number of essential clauses that should be included in every contract. These clauses include:
- Warranties: Warranties are promises by the supplier that the goods or services will meet certain standards.
- Indemnification: Indemnification clauses protect the buyer from liability in the event that the supplier breaches the contract.
- Dispute resolution: Dispute resolution clauses specify how disputes between the buyer and supplier will be resolved.
Contract Management and Compliance
Effective contract management and monitoring are crucial for ensuring that contracts are executed as intended and that both parties fulfill their obligations. Proper management helps organizations avoid disputes, protect their interests, and maintain strong relationships with suppliers.
Contract management involves tracking contract performance, identifying potential issues, and enforcing contract terms. By implementing a systematic approach, organizations can proactively manage contracts and ensure compliance.
Steps for Contract Management
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities: Define the roles and responsibilities of individuals involved in contract management, including the contracting officer, project manager, and legal counsel.
- Create a contract management plan: Develop a plan that Artikels the contract management process, including timelines, deliverables, and performance metrics.
- Monitor contract performance: Regularly review contract performance against agreed-upon metrics. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify any deviations from the expected outcomes.
- Identify potential issues: Proactively identify potential issues that may arise during contract execution. This may involve conducting risk assessments and monitoring industry trends.
- Enforce contract terms: Take appropriate action to enforce contract terms if necessary. This may involve issuing notices of default, seeking legal remedies, or negotiating amendments.
- Maintain contract documentation: Keep accurate and up-to-date contract documentation, including amendments, correspondence, and performance reports.
Supplier Relationship Management
SRM is a strategic approach to managing relationships with suppliers to create value for both parties. It goes beyond transactional interactions and focuses on building long-term partnerships that benefit both the buyer and the supplier.
Building strong supplier relationships can lead to a number of benefits, including:
- Improved communication and collaboration
- Increased trust and transparency
- Reduced costs and improved efficiency
- Enhanced innovation and product development
- Greater agility and responsiveness to changing market conditions
Strategies for Fostering Collaboration, Communication, and Trust
There are a number of strategies that buyers can use to foster collaboration, communication, and trust with their suppliers.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular communication | Buyers should communicate with their suppliers on a regular basis, both formally and informally. This helps to build relationships and ensure that both parties are on the same page. |
| Joint planning | Buyers and suppliers should work together to develop joint plans that Artikel their shared goals and objectives. This helps to align their interests and create a sense of共同所有权(ownership). |
| Information sharing | Buyers and suppliers should share information with each other openly and honestly. This helps to build trust and create a foundation for collaboration. |
| Problem solving | Buyers and suppliers should work together to solve problems that arise. This helps to build trust and demonstrate that both parties are committed to the relationship. |
| Performance evaluation | Buyers should evaluate their suppliers’ performance on a regular basis. This helps to ensure that suppliers are meeting expectations and that the relationship is beneficial to both parties. |
Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning
Protecting your business from potential risks associated with supplier contracts is crucial. Identifying these risks and implementing effective contingency plans will safeguard your operations.
Common risks include supply chain disruptions, quality issues, and financial instability. Mitigating these risks and developing contingency plans will minimize the impact on your business.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Disruptions |
|
| Quality Issues |
|
| Financial Instability |
|
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Supplier contracts carry significant legal and ethical implications. It is crucial to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, such as antitrust, data protection, and environmental standards. Failure to do so can result in severe consequences, including fines, reputational damage, and legal liability.
Guidelines for Legal and Ethical Compliance
The following table provides guidelines for ensuring compliance with legal and ethical obligations in supplier contracts:
| Legal/Ethical Consideration | Guideline |
|—|—|
| Antitrust | Prohibit agreements that restrict competition, such as price-fixing or market allocation. |
| Data Protection | Ensure compliance with data protection laws, such as GDPR, by safeguarding sensitive data and obtaining consent for its use. |
| Environmental Standards | Include provisions that promote environmental sustainability, such as waste reduction and energy efficiency. |
| Labor Practices | Prohibit unethical labor practices, such as child labor or forced labor. |
| Bribery and Corruption | Prohibit any form of bribery or corruption, including offering or accepting bribes. |
| Conflict of Interest | Disclose and manage any potential conflicts of interest that may arise during the contract period. |
By adhering to these guidelines, businesses can minimize legal and ethical risks associated with supplier contracts and maintain a reputation as a responsible and ethical organization.
Technology and Contract Management
In the modern business landscape, technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing contract management and compliance. By leveraging innovative software tools and platforms, organizations can streamline and automate various aspects of the contract lifecycle, ensuring greater efficiency, accuracy, and visibility.
Contract review, tracking, and reporting are key areas where technology can make a significant impact. Automated contract review tools use advanced algorithms to analyze contracts, identifying potential risks, inconsistencies, and non-compliance issues. This allows organizations to quickly and effectively assess contracts, reducing the risk of costly mistakes or disputes.
Contract Management Software Tools and Platforms
Numerous software tools and platforms are available to assist organizations with contract management. Here are a few examples:
- ContractWorks: A comprehensive contract management platform that offers features such as automated contract review, document generation, and compliance tracking.
- Ironclad: A cloud-based contract management solution that provides electronic signature capabilities, real-time collaboration, and AI-powered contract analysis.
- DocuSign CLM: A contract lifecycle management tool that includes features for contract creation, negotiation, execution, and storage.
By utilizing these advanced technologies, organizations can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their contract management processes, ensuring compliance, mitigating risks, and ultimately driving business success.
Contract Analytics and Performance Measurement
Data analytics plays a crucial role in contract management, enabling businesses to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and optimize supplier performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics for Supplier Performance Measurement
KPIs and metrics provide quantifiable measures to evaluate supplier performance and identify opportunities for improvement. Some key KPIs and metrics include:
- On-time delivery rate: Percentage of orders delivered within the agreed-upon time frame.
- Quality conformance rate: Percentage of products or services that meet the specified quality standards.
- Cost performance: Comparison of actual costs to agreed-upon prices, including any cost savings or overruns.
- Supplier responsiveness: Timeliness and effectiveness of supplier communication and support.
li>Customer satisfaction: Feedback from customers regarding the supplier’s performance.
By regularly tracking and analyzing these KPIs and metrics, businesses can identify areas where suppliers excel or fall short, and take steps to improve performance or address any issues.
FAQs
What are the key elements of a supplier contract agreement?
The key elements of a supplier contract agreement include the scope of work, payment terms, delivery schedules, performance guarantees, warranties, indemnification, and dispute resolution.
What are some best practices for negotiating a supplier contract?
Some best practices for negotiating a supplier contract include understanding your own needs and objectives, researching the supplier’s reputation and capabilities, and being prepared to walk away if the terms are not favorable.
What are the benefits of building strong supplier relationships?
The benefits of building strong supplier relationships include improved communication, collaboration, and trust, which can lead to better product quality, lower costs, and increased innovation.