Comprehensive Guide to Normal Radiology Report Templates
In the realm of medical imaging, radiology reports play a crucial role in communicating the findings of diagnostic examinations. These reports provide a detailed account of the images obtained, allowing clinicians to make informed decisions regarding patient care. Among the various types of radiology reports, normal radiology report templates hold a significant place, serving as standardized frameworks for describing unremarkable imaging findings.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of normal radiology report templates, exploring their structure, content, and clinical applications. By understanding the essential components and best practices associated with these templates, radiologists can ensure the accuracy, clarity, and consistency of their reporting, ultimately contributing to optimal patient management.
Template Structure

Normal radiology report templates are like a blueprint for writing radiology reports. They provide a consistent and organized framework for reporting the findings of medical imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
These templates typically include the following sections:
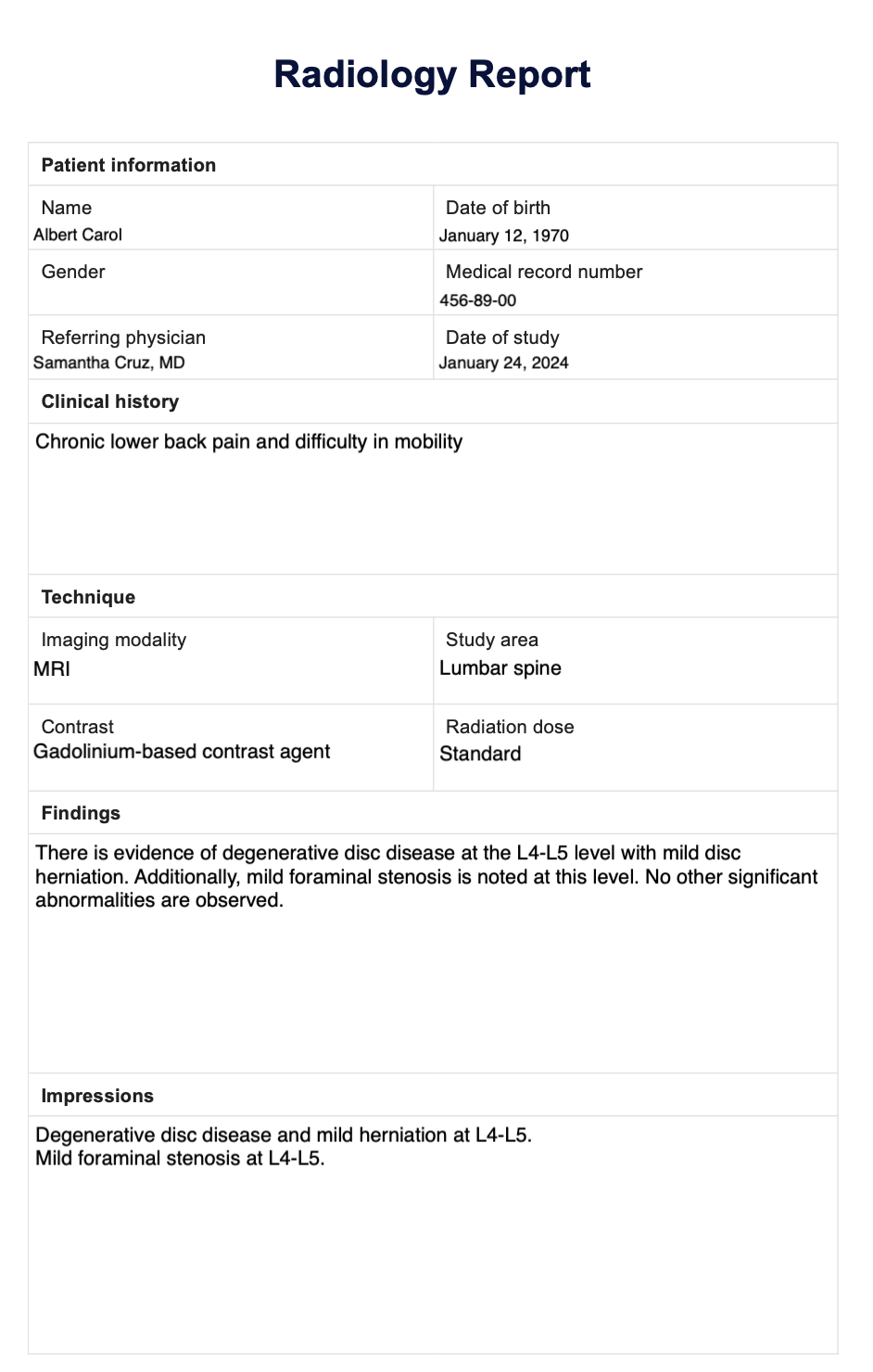
- Patient information: This section includes the patient’s name, date of birth, and other relevant information.
- Clinical history: This section includes a brief summary of the patient’s medical history, including the reason for the imaging study.
- Imaging findings: This section describes the results of the imaging study, including any abnormalities or variations from normal.
- Impression: This section provides a summary of the radiologist’s interpretation of the findings.
Standardization in template design is important because it helps to ensure that radiology reports are consistent and easy to read and understand. This is especially important for communication between radiologists and other healthcare providers, such as referring physicians and surgeons.
Imaging Findings
Imaging findings describe the observations made during the interpretation of medical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. These findings help radiologists assess the normalcy or abnormality of the anatomy and identify any potential underlying conditions.
Normal imaging findings are characterized by the absence of any significant abnormalities or deviations from the expected anatomy. Radiologists use specific descriptive terms and phrases to convey the normal appearance of anatomical structures.
Descriptive Terms and Phrases
Descriptive terms used in normal radiology reports include:
- Normal: Indicates that the anatomical structure is within expected limits and shows no signs of abnormality.
- Unremarkable: Similar to “normal,” indicating that nothing unusual or concerning was observed.
- Symmetrical: Describes structures that are mirror images of each other, as expected in normal anatomy.
- Smooth: Indicates that the margins or surfaces of structures are even and regular, without any irregularities.
- Homogeneous: Refers to structures that have a uniform density or texture throughout.
Modality-Specific Terminology
Specific imaging modalities may use different terminology to describe normal findings:
- X-ray:
- Clear lungs: No evidence of infiltrates, nodules, or other abnormalities.
- Normal heart size: Heart shadow within expected dimensions.
- CT:
- No enhancing lesions: Absence of any abnormal areas that enhance with contrast.
- Homogeneous liver parenchyma: Uniform density and texture of the liver tissue.
- MRI:
- T1-weighted images: Normal signal intensity of various tissues, such as white matter appearing bright and gray matter appearing dark.
- T2-weighted images: Normal fluid-filled structures, such as cerebrospinal fluid, appearing bright.
Impression and Interpretation
Impression and interpretation are essential sections of normal radiology reports, where radiologists summarize their findings and provide their professional opinions on the patient’s condition. The impression section serves as a concise statement that conveys the overall assessment of the radiologist.
In normal radiology reports, radiologists typically convey their interpretations using standardized phrases and templates. These standardized phrases have been carefully crafted to accurately and efficiently describe normal findings, ensuring consistency and clarity in reporting.
Use of Standardized Phrases and Templates
Standardized phrases and templates are used for normal interpretations to:
- Ensure accuracy and consistency in reporting.
- Facilitate quick and easy interpretation by referring clinicians.
- Reduce the risk of misinterpretation or confusion.
These standardized phrases and templates are often derived from consensus guidelines and established medical terminology, ensuring their validity and reliability.
Report Formatting
Standardised formatting in radiology reports ensures efficient reporting and improves communication between radiologists and referring clinicians. It allows for quick identification of key information and facilitates comparison of findings over time.
A common formatting structure for normal radiology reports includes the following elements:
Table of Common Formatting Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Patient Information | Patient’s name, age, gender, medical record number |
| Examination Details | Type of examination, date and time, body part examined |
| Findings | Description of the imaging findings, including normal anatomy and any incidental findings |
| Impression | Summary of the findings and any relevant clinical implications |
Quality Control and Standardization
Maintaining high-quality standards in normal radiology reporting is crucial. This ensures accuracy, consistency, and timely delivery of reports.
Peer Review and Audits
Peer review involves the examination of reports by another qualified radiologist to verify accuracy and completeness. This helps identify and correct any discrepancies or errors. Audits, on the other hand, assess the overall quality of reporting practices and adherence to established guidelines.
Standardized Templates and Protocols
Standardized templates and protocols provide a structured framework for reporting. They ensure consistency in the format, terminology, and organization of reports, making them easier to interpret and compare. This also reduces variability and promotes efficiency in the reporting process.
Clinical Applications
Normal radiology reports are essential tools in patient management, providing valuable information to clinicians for diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up care.
These reports are used in a wide range of clinical settings, including:
- Emergency medicine: To rapidly assess and triage patients with acute injuries or illnesses.
- Inpatient care: To monitor disease progression, evaluate treatment response, and detect complications.
- Outpatient care: To screen for disease, diagnose conditions, and provide follow-up care.
Clear and concise reporting is crucial for effective communication with clinicians. Accurate and detailed descriptions of imaging findings allow clinicians to make informed decisions about patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key sections typically included in normal radiology report templates?
Normal radiology report templates typically include sections for patient information, examination details, imaging findings, impression, and interpretation.
Why is standardization important in the design of normal radiology report templates?
Standardization in the design of normal radiology report templates promotes consistency, reduces variability, and ensures that all relevant information is included in a logical and easy-to-understand format.
How do radiologists convey their interpretations of normal findings in normal radiology reports?
Radiologists convey their interpretations of normal findings using descriptive terms and phrases that accurately reflect the absence of abnormalities or the presence of expected anatomical structures.
What are the benefits of using standardized formatting for normal radiology reports?
Standardized formatting for normal radiology reports improves readability, facilitates efficient reporting, and reduces the risk of errors.
How do quality control measures ensure the accuracy of normal radiology reports?
Quality control measures such as peer review and audits help to identify and correct any errors or inconsistencies in normal radiology reports, ensuring their accuracy and reliability.