Radiology Report Templates: Essential Tools for Accurate and Efficient Reporting
Radiology report templates are indispensable tools that streamline the reporting process, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and efficiency in radiology departments. These templates provide a structured framework for radiologists to document their findings, facilitating clear communication with referring physicians and patients.
The adoption of radiology report templates has surged in recent years, with studies indicating a significant reduction in reporting errors and improved turnaround times. This has not only enhanced patient care but also optimized workflow and increased productivity within radiology practices.
Introduction
Radiology report templates are essential tools that streamline the creation of standardized and consistent radiology reports. These templates provide a structured framework that guides radiologists in reporting medical imaging findings, ensuring accuracy, completeness, and clarity in communication with referring clinicians and patients.
The use of radiology report templates has been widely adopted in clinical practice, with studies indicating that they significantly improve the quality and efficiency of reporting. They promote consistency in language, terminology, and reporting style, reducing variability and minimizing the risk of misinterpretation.
Benefits of Radiology Report Templates
- Enhanced Accuracy: Templates ensure that all essential information is included in the report, reducing the likelihood of omissions or errors.
- Improved Clarity: Standardized language and formatting enhance clarity, making reports easier to read and understand for both clinicians and patients.
- Increased Efficiency: Predefined templates save time and effort, allowing radiologists to focus on interpreting images rather than formatting reports.
- Reduced Variability: Templates minimize variations in reporting style, promoting consistency and reducing the risk of miscommunication.
- Improved Communication: Standardized templates facilitate effective communication between radiologists and referring clinicians, ensuring that key findings are conveyed clearly.
Types of Radiology Report Templates
Radiology report templates provide a structured framework for radiologists to document their findings and impressions. There are several types of templates available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Free-Text Templates
Free-text templates allow radiologists to create reports using their own language and formatting. This flexibility can be advantageous for complex cases or when specific details need to be highlighted.
However, free-text templates can also lead to inconsistencies in reporting and make it difficult to compare findings across different reports.
Example: A free-text template might include sections for patient demographics, clinical history, imaging findings, and impressions.
Structured Templates
Structured templates provide a more standardized approach to reporting. They use predefined sections and fields, which helps to ensure consistency and completeness.
Structured templates can improve efficiency and reduce the risk of errors. However, they can also be less flexible and may not allow for the inclusion of all relevant information.
Example: A structured template might include a checklist of common findings, as well as fields for free-text comments.
Hybrid Templates
Hybrid templates combine elements of both free-text and structured templates. They provide a balance of flexibility and standardization.
Hybrid templates can be customized to meet the specific needs of a particular practice or department. However, they can also be more complex to create and maintain.
Example: A hybrid template might include a structured section for common findings, followed by a free-text section for additional comments.
Elements of a Radiology Report Template

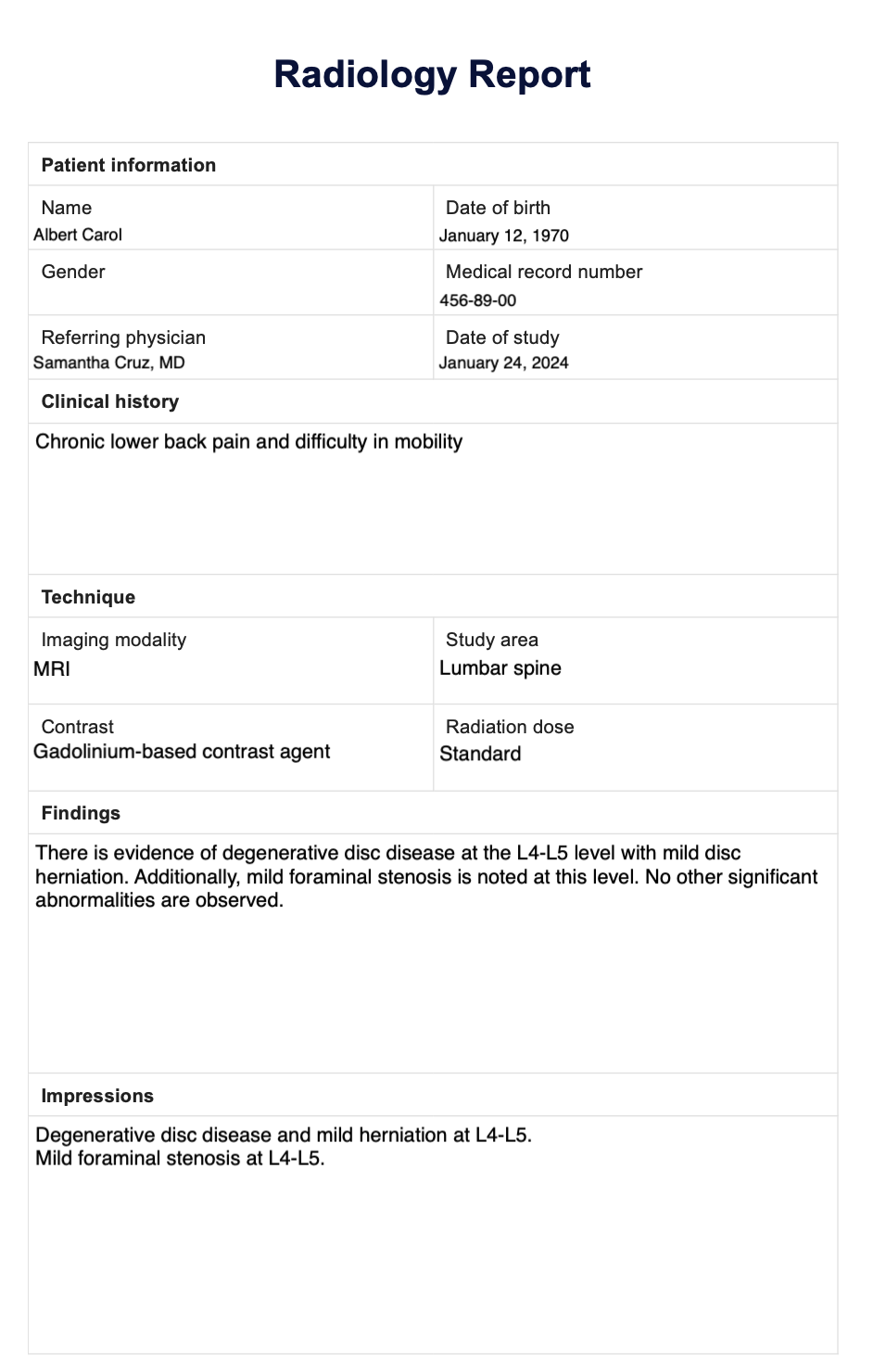
Every radiology report template consists of essential elements that provide a structured framework for presenting findings and impressions. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective communication and interpretation of radiology reports.
Patient Information
- Patient’s name, age, and gender: Identifies the patient and provides context for the examination.
- Date of examination: Indicates when the examination was performed.
- Reason for examination: States the clinical question or indication for the study.
Technical Information
- Modality: Specifies the imaging technique used, such as X-ray, CT, MRI, or ultrasound.
- Equipment settings: Provides information about the parameters used during the examination, such as kVp, mA, slice thickness, and field of view.
- Contrast agent: Indicates if a contrast agent was administered and the type of contrast used.
Findings
This section describes the observations made during the examination. It should be organized and detailed, using appropriate medical terminology and anatomical landmarks.
Impression
The impression summarizes the key findings and provides a diagnostic interpretation. It should be concise and clear, stating the most likely diagnosis or differential diagnoses.
Additional Information
This section includes any additional comments, recommendations, or limitations of the examination. It may also contain information about follow-up studies or consultations.
Customization of Radiology Report Templates
Customizing radiology report templates is key for efficient and accurate reporting. It streamlines the process, reduces errors, and improves consistency.
Guidelines for Effective Customization
– Identify specific requirements and workflows.
– Collaborate with radiologists to define template structure and content.
– Consider the type of imaging modality and clinical setting.
– Use standardized terminology and abbreviations.
– Implement automated features for data entry and calculations.
Best Practices for Accuracy and Consistency
– Establish a template approval process.
– Provide training and support for template users.
– Regularly review and update templates to ensure they align with current practices.
– Use validation tools to check accuracy and consistency.
– Encourage feedback from users to continuously improve templates.
Integration with Radiology Information Systems
Integrating radiology report templates with radiology information systems (RIS) brings numerous advantages. Firstly, it streamlines the reporting process, allowing radiologists to access patient data, images, and previous reports effortlessly. Secondly, it enhances report consistency and quality by enforcing standardized templates and reducing transcription errors. Thirdly, it facilitates efficient data sharing and collaboration among healthcare providers.
However, integration poses certain challenges. Technical compatibility, data security, and workflow disruptions must be carefully considered. Additionally, training and user adoption can be critical factors for successful integration.
Despite these challenges, successful integrations have been achieved. For instance, the integration of structured reporting templates with a RIS at a large hospital led to a significant reduction in reporting time and improved report quality. Another example is the seamless integration of a cloud-based RIS with a reporting system, enabling remote access and collaboration among radiologists across multiple locations.
Quality Control and Maintenance
Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of radiology reports is paramount for patient safety and quality of care. Radiology report templates play a vital role in this process by providing a standardized framework for reporting. However, it’s crucial to implement robust quality control measures to guarantee the templates’ reliability and effectiveness.
Steps Involved in Quality Control
A comprehensive quality control process for radiology report templates should encompass the following steps:
- Validation: Verify that the templates adhere to established guidelines and best practices, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to identify and rectify any potential errors or inconsistencies within the templates.
- Review: Regularly review and evaluate the templates to assess their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
To maintain the integrity and relevance of radiology report templates, ongoing maintenance and updates are essential. This involves:
- Regular Updates: Regularly update the templates to incorporate advancements in medical knowledge and technology.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from radiologists and other stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and enhancement.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of the templates to ensure they meet the evolving needs of radiology practice.
By implementing a robust quality control and maintenance program for radiology report templates, healthcare providers can ensure the accuracy, consistency, and effectiveness of their reporting, ultimately enhancing patient care and safety.
Q&A
What are the different types of radiology report templates available?
Radiology report templates can be categorized into general templates, body part-specific templates, and disease-specific templates. General templates provide a basic framework for reporting on various body parts, while body part-specific templates are tailored to specific anatomical regions, such as the chest, abdomen, or musculoskeletal system. Disease-specific templates are designed for reporting on specific diseases or conditions, such as cancer or trauma.
How can I customize radiology report templates to meet my specific needs?
Customizing radiology report templates involves modifying the content, structure, and layout to align with the preferences and requirements of individual radiologists or departments. This can include adding or removing sections, altering the order of elements, and incorporating custom macros or phrases. It is important to ensure that customizations do not compromise the accuracy or completeness of the report.
What are the benefits of integrating radiology report templates with radiology information systems?
Integrating radiology report templates with radiology information systems (RIS) offers numerous advantages. It enables seamless data transfer between the reporting system and the RIS, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. Additionally, integration facilitates the automated generation of reports, streamlines workflow, and enhances overall efficiency.